EddyXpert - Eddy current separators
Search results
Your results in: pages, products and documents
Scroll to see everything. Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try another search term or contact us.
No results found

-
{{filter.Description}}
({{filter.UOMDescription}})








No results found
Your results in: pages, products and documents
Scroll to see everything. Didn't find what you were looking for?
Try another search term or contact us.
Application EddyXpert - eddy current separators
They purify large bulk streams and/or separate non-ferrous metals for reuse. Eddy current separators have many uses. They can handle high capacities, because the conveyor belt separates and carries away non-ferrous metals continuously and fully automatically.
An important factor for good separation is an even flow of material, supplied by a vibratory feeder or conveyor belt for example. This results in a uniform distribution across the belt, so that the material arrives as a mono-layer. This means that the supplied layer thickness is about as thick as the largest piece, and thus that there are no pieces lying one on top of the other. This is especially important with smaller fraction sizes. Goudsmit separators are robustly built so they can remain operational day and night in even the most demanding applications, such as incinerator slag reprocessing.
Application of the EddyXpert include:
- recovery of coarse to fine non-ferrous metals from slag from waste incineration plants
- recovery of precious metals from scrap or electronics waste
- recovery of casting residues in the metal casting industry
- elimination of metals out of shredded wood chips
- elimination of aluminium for the glass recycling industry
- elimination of impurities from recycled plastic streams for protection of injection moulding machines

Separation of metals
There are two factors that influence the separation of metals:
Material
Some non-ferrous metals are more easily separated than others. This has to do with the physical properties. This table lists non-ferrous metals categorized on the basis of three factors. The first column shows the electrical conductivity of the material: a measure of how easily a material conducts electricity. The second column indicates the density of the material. This is important for the effect of gravity on the ejected piece of metal. After all, the Eddy current forces generated by the Eddy current magnet roller must overcome these forces. The last column shows the ratio between these two factors. The greater the electrical conductivity and the lower the density, the better a material can be separated with the Eddy current technique.
Size and shape
The fraction size (i.e. the size of the particles in the flow of material) is also a very important factor for achieving good separation. Eddy currents induce repulsive forces in a piece of metal that cause it to be ejected with a certain trajectory. As a result, the non-ferrous metals have a different ejection trajectory than the other residue and inert materials in the product stream. This ultimately results in a ‘range of trajectories’ for inert and non-ferrous material. The larger the volume, the more widely ‘separated’ the ejection trajectories of a chunk of inert material and a non-ferrous metal object of the same volume. This is why it is easier to separate aluminium cans than small copper wires. Size plays a role, as does the shape. For example, a ball has less air resistance than a tangle of copper wire or a bent piece of sheet metal.
| Material | Electric conductivity | Density | Conductivity/Density |
|---|---|---|---|
| σ = [1/Ω x m] | ρ = [kg/m3] | σ / ρ = [m2/kg x Ω] | |
| x 106 | x 103 | ||
| Non ferro metals | |||
| Aluminium | 37,0 | 2700 | 13,7 |
| Magnesium | 21,7 | 1740 | 12,5 |
| Copper | 59,9 | 8960 | 6,7 |
| Silver | 62,1 | 10500 | 5,9 |
| Zinc | 16,9 | 7140 | 2,4 |
| Gold | 41,7 | 19320 | 2,2 |
| Brass | 15,2 | 8500 | 1,8 |
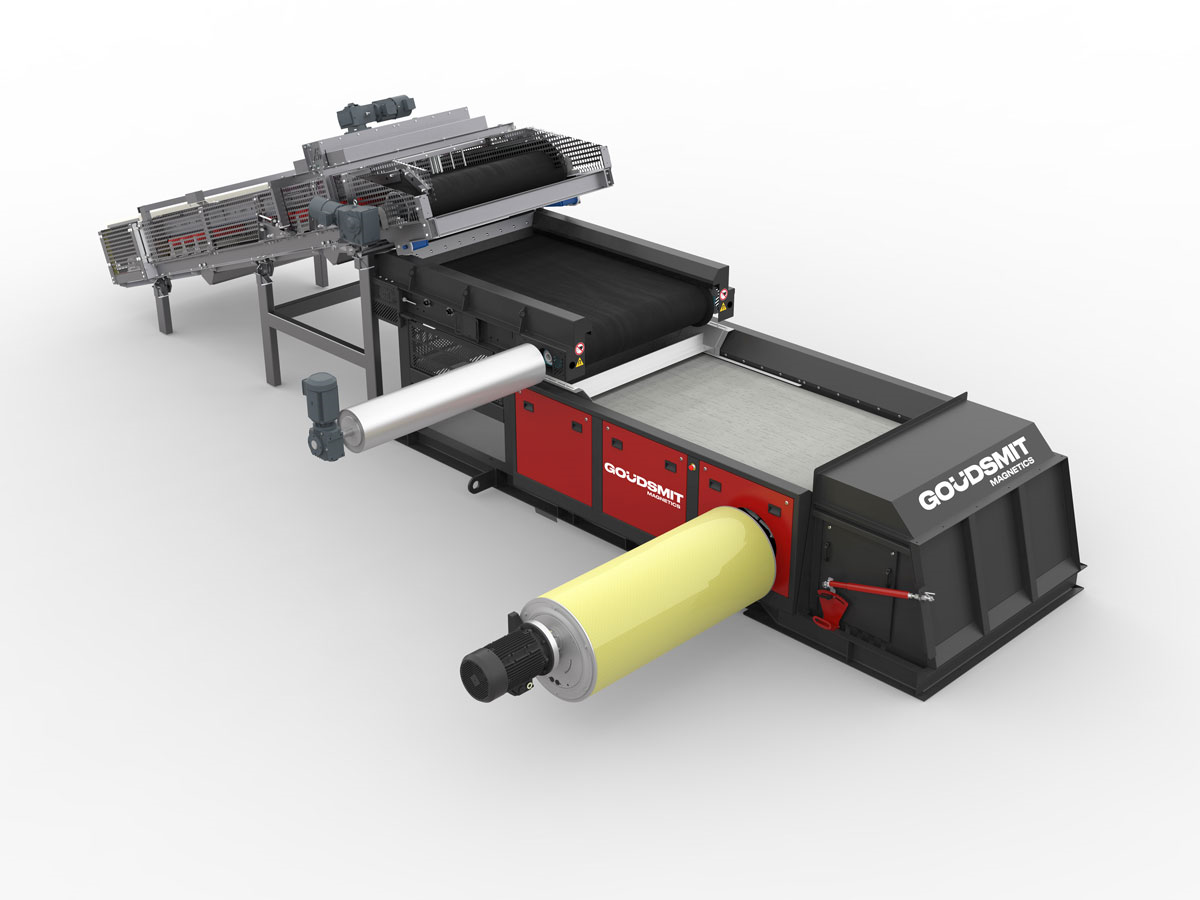
Design of the EddyXpert
Conveyor belt
The EddyXpert separators can be equipped with 3 types of conveyor belts:
- PU conveyor belt: on average, these have a 2x longer lifespan than the less durable and cheaper PVC conveyor belts. We prefer these belts because they are durable and can be produced thin. A thin conveyor belt has the advantage that the magnetic force is higher, which in turn results in a better separation of metals.
- Rubber conveyor belt: These belts are a lot thicker, which reduces the magnetic force on the belt surface. Rubber is resilient and can absorb the impact of sharp or large parts.
- PVC conveyor belt: These belts are the cheapest and the least durable.
Slide plates
Non ferrous metals will be separated better when they lay still at the separation point of the Eddy current magnet roller. Therefore the conveyor belt is supported by stainless steel sliding plates, which ensure flat and stable transportation of the material. Competitors use conveyor belt support rollers which make materials bounce which has a negative effect on separation. They also add extra maintenance to the machine, because the bearings of the support rollers need to be changed.
Integrated drum motor
An integrated drum motor provides the drive for the conveyor belt. This provides a compact design, because there is no motor protruding from the rear of the machine. This drum motor has an IP66 protection rating, so it is well protected against dust and moisture. This means that the motor is virtually maintenance-free, which contributes to making this a robust and user-friendly machine, a fact that will surely be appreciated by your operators.
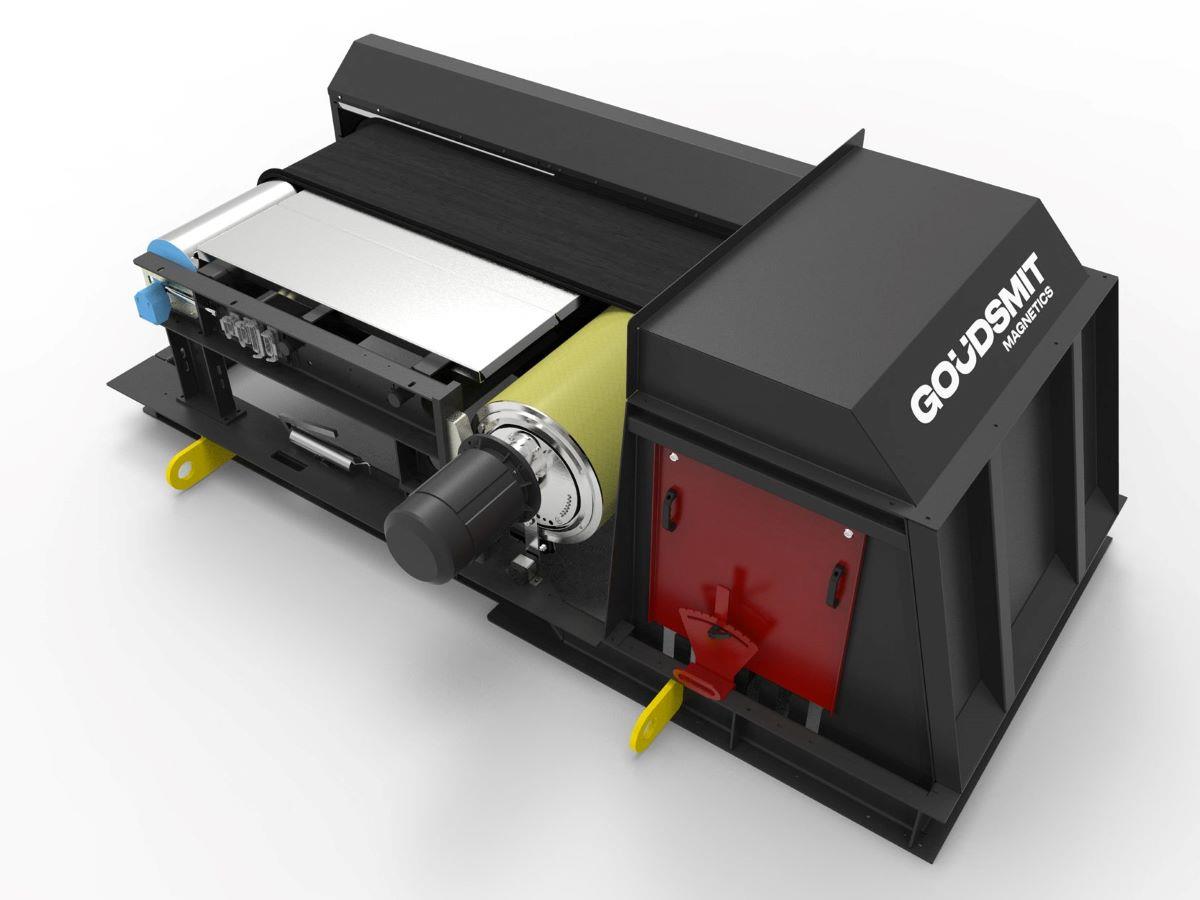

Working principle of eddy current separation
Eddy current separators have a conveyor belt system with a high-speed magnetic rotor at the end. The rotation speed of the magnets generates an induction field, creating a rapidly changing magnetic field. See animation. The separation is based on the principle that every electrically conductive particle located in an alternating magnetic field is temporarily magnetized. Simply put: for a brief moment all metals that pass the Eddy current magnet roller become magnetized themselves, causing them to be ejected. This enables us to separate a huge number of non-ferrous metals and their alloys, including aluminium, copper and brass.
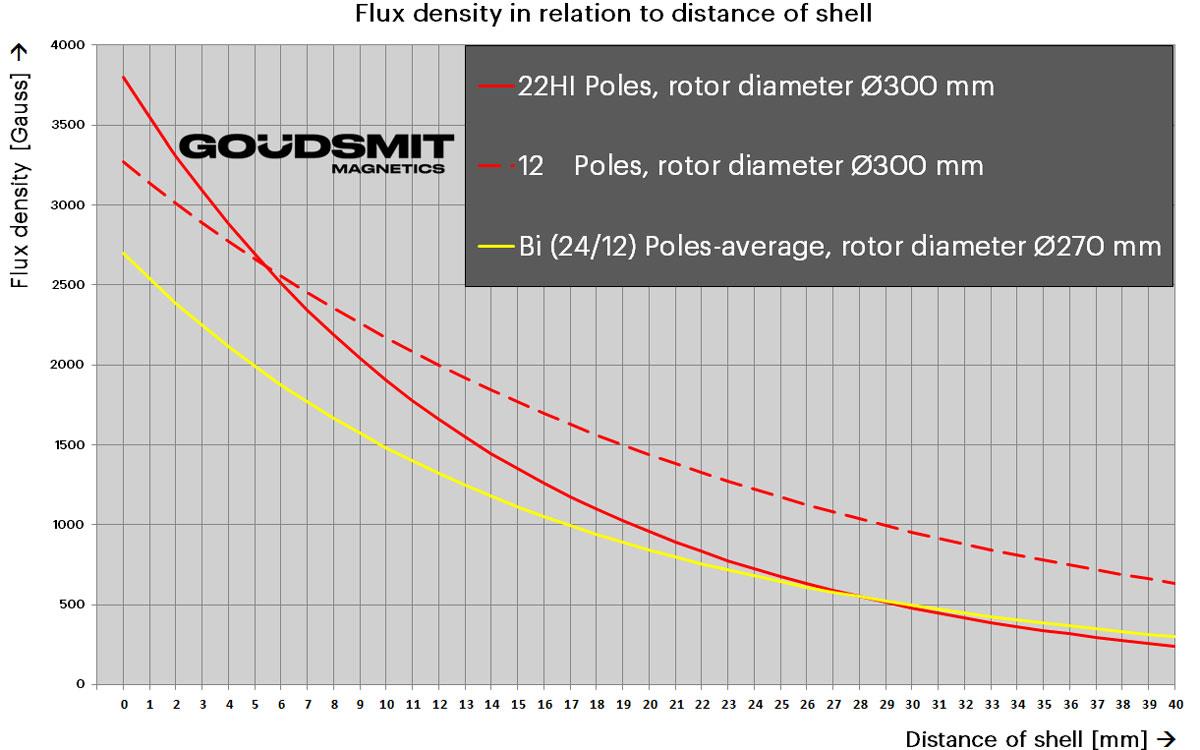
Flux density of various EddyXpert magnet rollers
With the EddyXpert, you can choose between two different Eddy current magnet rotors:
- 12-pole: deep, powerful magnetic field and relatively few pole changes. The 12-pole serves coarse material flows with a fraction of 20-300 mm. Its deep field makes it the perfect pre-separator.
- 22HI pole: shallower field than the 12 pole, but higher magnetic force and many more pole changes close to the belt surface.
This makes the 22HI suitable for material flows with a fraction of 5-60+ mm. Do you want to separate smaller than 5 mm? Then take a look at the EddyFines.
The table shows how the two Eddy current magnet rotors compare to each other and other suppliers. The Y axis shows the magnetic force (flux density in gauss) plotted against the distance of the tube on the X axis. Add the thickness of the belt from zero and you know what the flux density on the belt surface is. The graph shows the effect of economising on magnetic material: the most expensive component in these machines. At Goudsmit, we know that the right use of magnetic material creates the perfect separation. That translates to magnet volume and pole number.
HI (High Intensity)
Some of Goudsmit's eddy current magnet rotors, such as the 22HI and the 38HI, feature an HI magnet configuration. Goudsmit sets itself apart with this technology, which generates extremely high magnetic forces. The HI magnet rotors can therefore also be used for fractions that are difficult to process or difficult to separate non-ferrous particles.
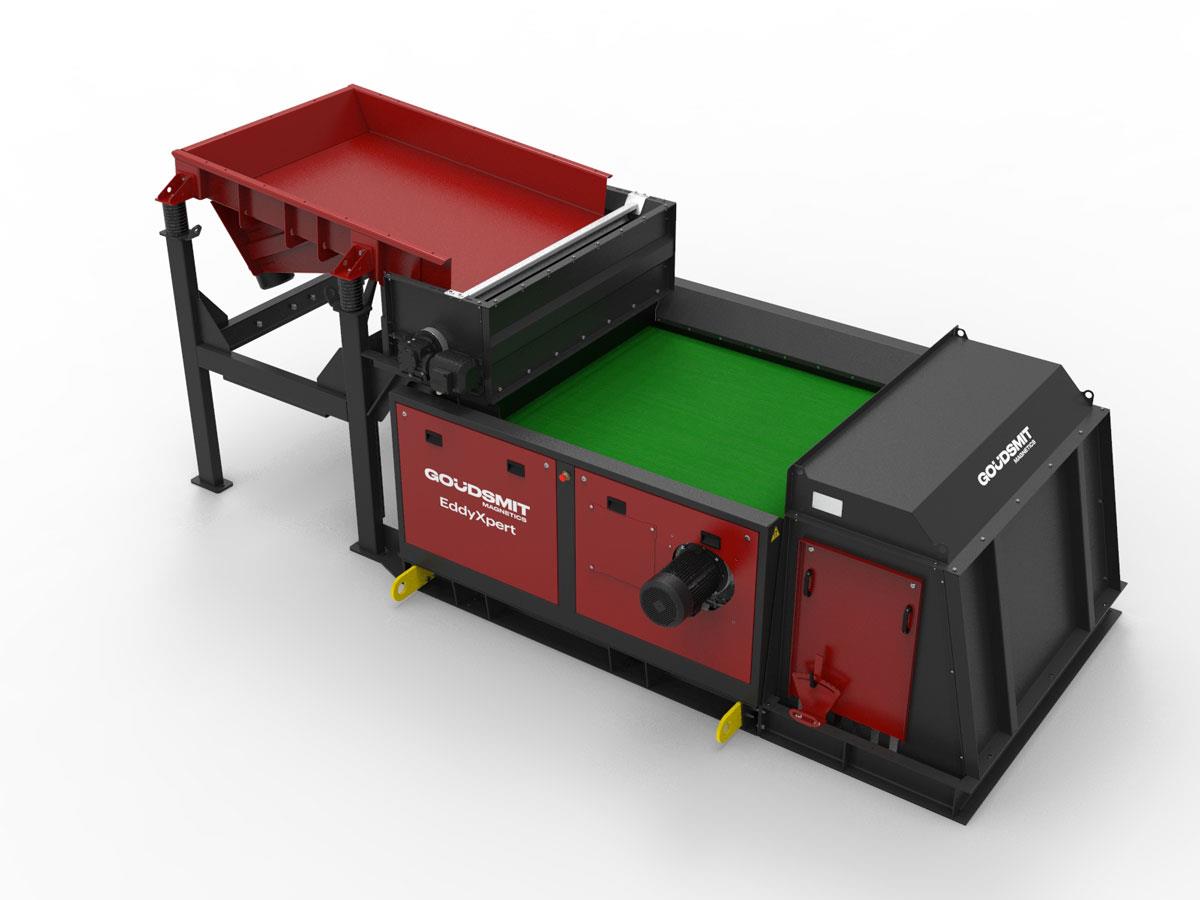
Feeder module EddyXpert
The function of the supply segment is the uniform supply of material the creation of a mono-layer. A good supply of material is crucial for separation of the non-ferrous metals. If other material is lying on top of the non-ferrous pieces it is more difficult to eject them over the partition. Depending on your product stream, you can choose from various supply modules:
Vibratory feeder
The vibratory feeder is the most frequently chosen option. It supplies the product stream to the Eddy current as a uniform (i.e. distributed across the width) mono-layer. If your product stream still contains ferrous pieces, we can expand the vibratory feeder to include a deferrization module such as a drum magnet. This causes the material to fall evenly onto the drum; the ferromagnetic pieces are separated and the rest of the product stream (including non-ferrous metals) moves on to the conveyor belt of the middle unit. For the drum magnet there is a choice of different magnetic strengths, so we can always guarantee optimal separation. The vibratory feeder module is not suitable for incinerator slag due to the sticking of the cementitious mass.

Conveyor belt module
The conveyor belt module has an integrated magnetic head pulley. This provides efficient removal of the pieces of ferrous metal still remaining in the supplied product stream. The magnetic head roller can be made with various types (strengths) of magnet. So we can guarantee the best solution for your product stream. One of the advantages of the conveyor belt module is that it is independently adjustable in speed. This is crucial for adjusting the ferrous separation. Another additional advantage is the integrated belt scraper that continuously cleans the belt from sticky materials such as bottom ashes. Note: for the distribution of the material, an additional spreader belt with 'material spreaders' is needed.
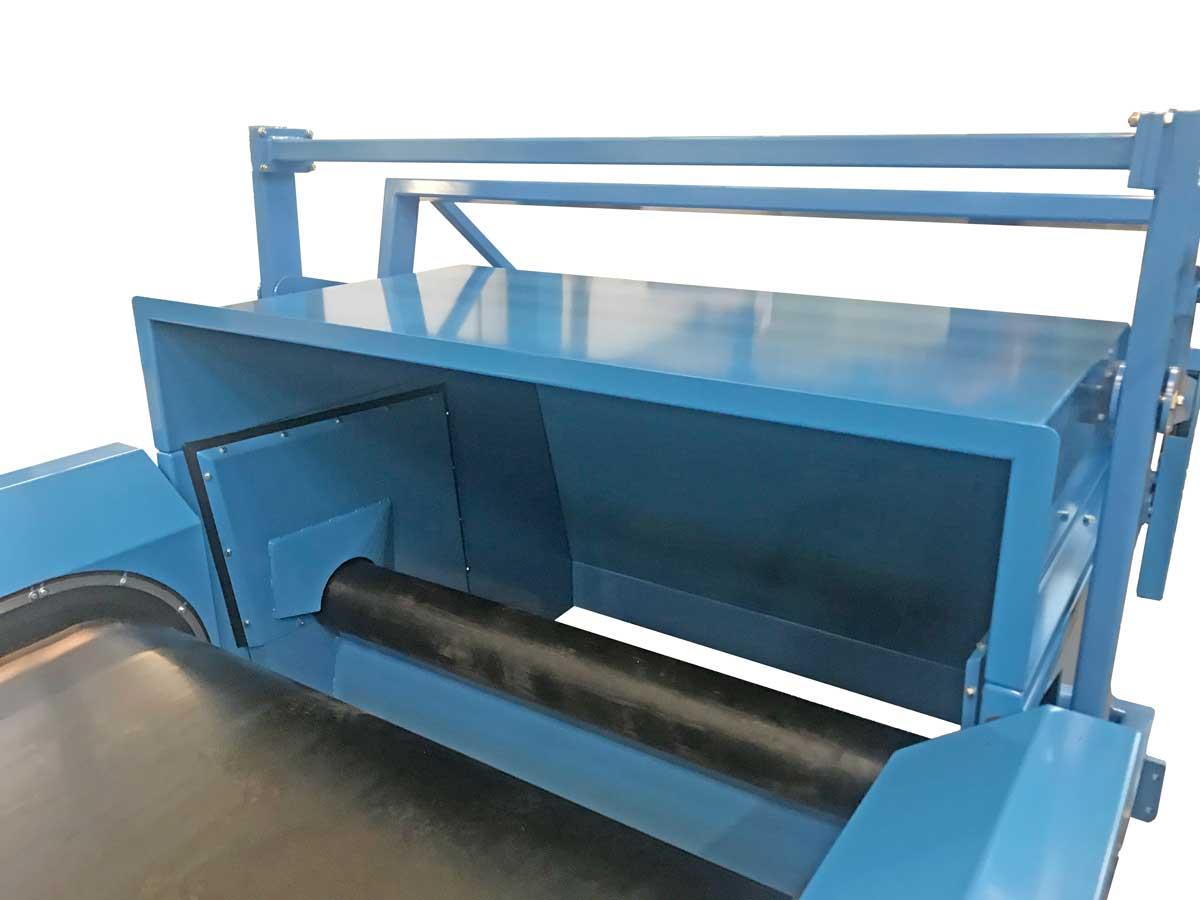
Separation plate / splitter
For the final, definitive separation of the two product streams we place a separation plate between the inert and non-ferrous streams. The parts of the separation plate that are in contact with the material are executed in manganese steel. This material is self hardening for long service life. There are different types of end tips or plates to ensure maximum separation or purity of your product stream.
Rotating top roller
This separation plate is used in coarse product streams that contain long flexible parts, such as cables or plastic bags. The rotating top roller turns these parts away so that the separation point remains pure.

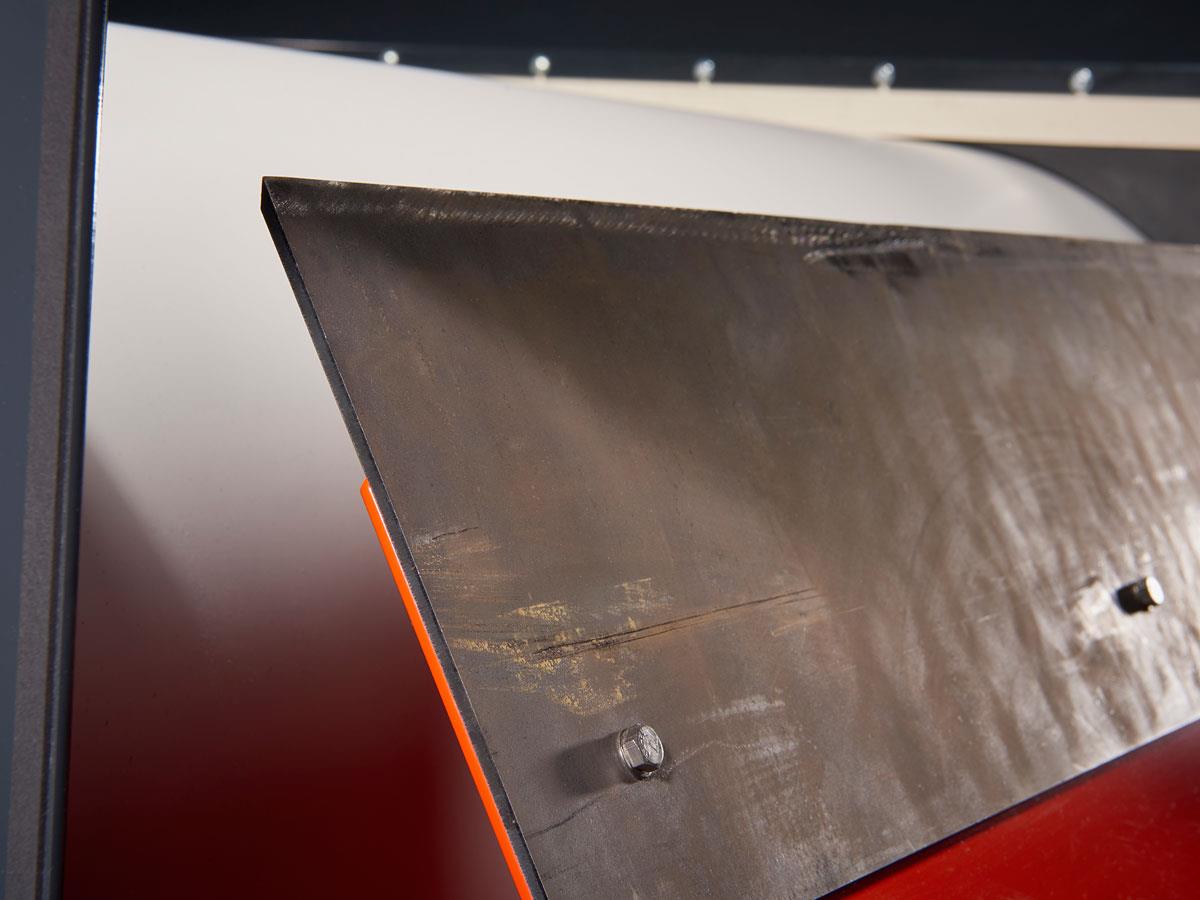
Manganese steel fines plate
This plate is often used in abrasive product streams like: incineration slags or scrap metals. The tip is very sharp for precise separation. The manganese steel is a self hardening material so the tip stays sharp for a long time.

Trespa fines plate
This plate is often used in light product streams that do not have a large impact on the tip, like for example: PET flakes or rubber granulate. The plate is also sharp but the main advantage is that this material isnon conductive. Therefore, the separation point can be set really close to alternating magnetic Eddy current field without getting heated. This creates the best separation degree.


The eddy current separator type EddyXpert is the all-rounder of the ECS machine line and is suitable for a large number of product streams: from coarse to medium-fine fractions. Many possible combinations for desired application.